Contents
- Getting Started
- External database for pgAdmin user settings
- Connecting To A Server
- Managing Cluster Objects
- Managing Database Objects
- Cast Dialog
- Using EDB Job Scheduler
- Collation Dialog
- Domain Dialog
- Domain Constraints Dialog
- Event Trigger Dialog
- Extension Dialog
- Foreign Data Wrapper Dialog
- Foreign Server Dialog
- Foreign Table Dialog
- FTS Configuration Dialog
- FTS Dictionary Dialog
- FTS Parser Dialog
- FTS Template Dialog
- Function Dialog
- Language Dialog
- Materialized View Dialog
- Package Dialog
- Procedure Dialog
- Publication Dialog
- Schema Dialog
- Sequence Dialog
- Subscription Dialog
- Synonym Dialog
- Trigger Function Dialog
- Type Dialog
- User Mapping Dialog
- View Dialog
- Creating or Modifying a Table
- Management Basics
- Backup and Restore
- Developer Tools
- Processes
- pgAgent
- pgAdmin Project Contributions
- Release Notes
- Licence
Event Trigger Dialog¶
Use the Event Trigger dialog to define an event trigger. Unlike regular triggers, which are attached to a single table and capture only DML events, event triggers are global to a particular database and are capable of capturing DDL events. Like regular triggers, event triggers can be written in any procedural language that includes event trigger support, or in C, but not in SQL.
The Event Trigger dialog organizes the development of a event trigger through the following dialog tabs: General, Definition, and Security Labels. The SQL tab displays the SQL code generated by dialog selections.
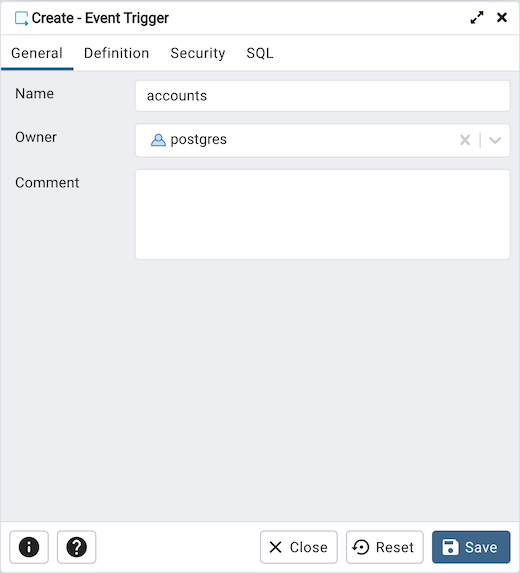
Use the fields in the General tab to identify the event trigger:
Use the Name field to add a descriptive name for the event trigger. The name will be displayed in the pgAdmin tree control.
Use the drop-down listbox next to Owner to specify the owner of the event trigger.
Store notes about the event trigger in the Comment field.
Click the Definition tab to continue.
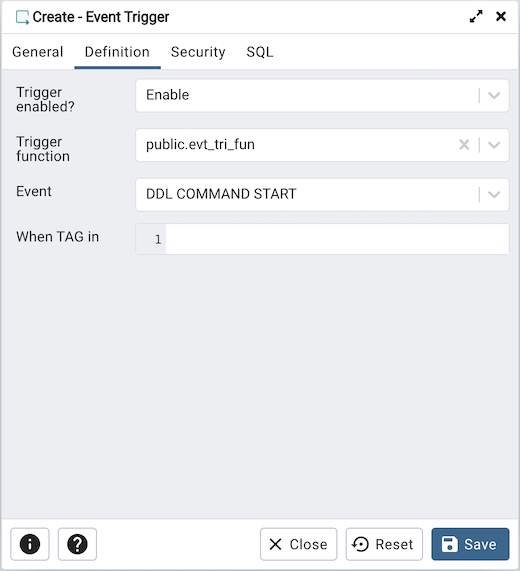
Use the fields in the Definition tab to define the event trigger:
Select a value from the drop down of Trigger Enabled field to specify a status for the trigger: Enable Disable, Replica Always.
Use the drop-down listbox next to Trigger function to specify an existing function. A trigger function takes an empty argument list, and returns a value of type event_trigger.
Select a value from the drop down of Events field to specify when the event trigger will fire: DDL COMMAND START, DDL COMMAND END, or SQL DROP.
Use the When TAG in field to enter filter values for TAG for which the trigger will be executed. The values must be in single quotes separated by comma.
Click the Security Labels tab to continue.
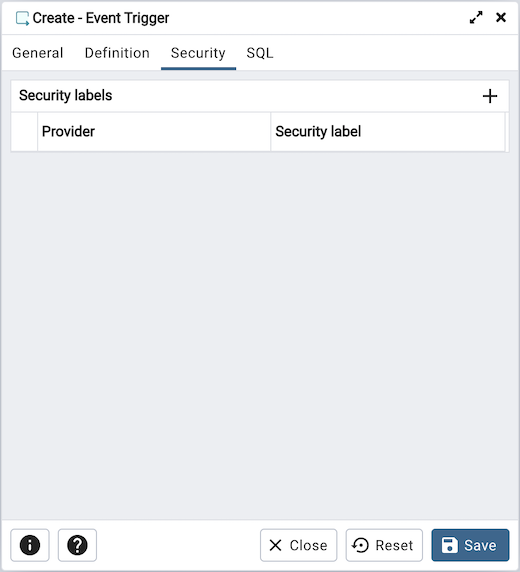
Use the Security tab to define security labels applied to the trigger. Click the Add icon (+) to add each security label.
Specify a security label provider in the Provider field. The named provider must be loaded and must consent to the proposed labeling operation.
Specify a security label in the Security Label field. The meaning of a given label is at the discretion of the label provider. PostgreSQL places no restrictions on whether or how a label provider must interpret security labels; it merely provides a mechanism for storing them.
Click the Add icon (+) to assign additional security labels; to discard a security label, click the trash icon to the left of the row and confirm deletion in the Delete Row popup.
Click the SQL tab to continue.
Your entries in the Event Trigger dialog generate a generate a SQL command. Use the SQL tab for review; revisit or switch tabs to make any changes to the SQL command.
Example¶
The following is an example of the sql command generated by user selections in the Event Trigger dialog:
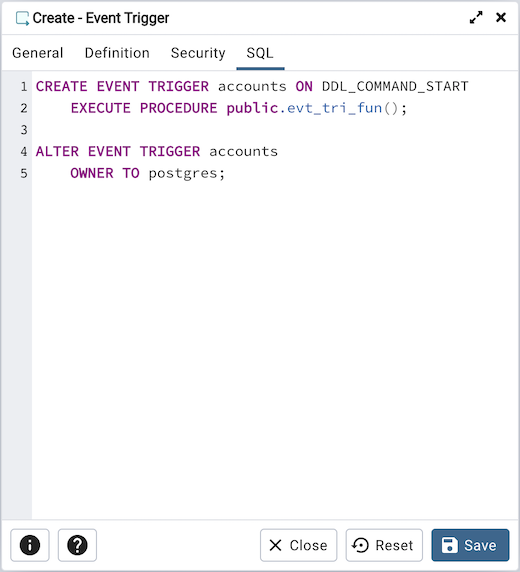
The command creates an event trigger named accounts that invokes the procedure named evt_tri_fun.
Click the Info button (i) to access online help.
Click the Save button to save work.
Click the Close button to exit without saving work.
Click the Reset button to restore configuration parameters.