Query Tool¶
The Query Tool is a powerful, feature-rich environment that allows you to execute arbitrary SQL commands and review the result set. You can access the Query Tool via the Query Tool menu option on the Tools menu, or through the context menu of select nodes of the Object explorer control. The Query Tool allows you to:
Issue ad-hoc SQL queries.
Execute arbitrary SQL commands.
Edit the result set of a SELECT query if it is updatable.
Displays current connection and transaction status as configured by the user.
Save the data displayed in the output panel to a CSV file.
Review the execution plan of a SQL statement in either a text, a graphical format or a table format (similar to https://explain.depesz.com).
View analytical information about a SQL statement.
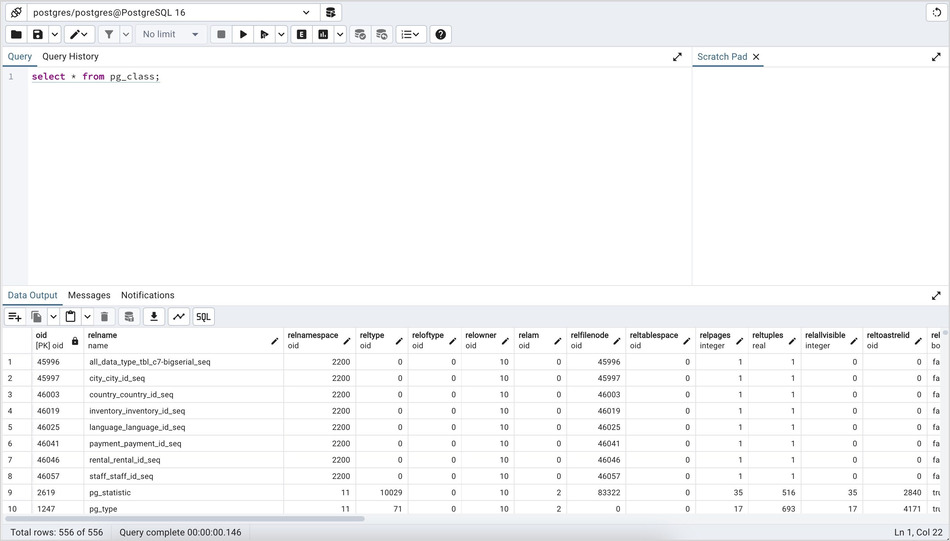
You can open multiple copies of the Query tool in individual tabs simultaneously. To close a copy of the Query tool, click the X of the tab.
The Query Tool features two panels:
The upper panel displays the SQL Editor. You can use the panel to enter, edit, or execute a query or a script. It also shows the History tab which can be used to view the queries that have been executed in the session, and a Scratch Pad which can be used to hold text snippets during editing. If the Scratch Pad is closed, it can be re-opened (or additional ones opened) by right-clicking in the SQL Editor and other panels and adding a new panel.
The lower panel displays the Data Output panel. The tabbed panel displays the result set returned by a query, information about a query’s execution plan, server messages related to the query’s execution and any asynchronous notifications received from the server.
Toolbar¶
The toolbar is described in the following subsections.
The SQL Editor Panel¶
The SQL editor panel is a workspace where you can manually provide a query, copy a query from another source, or read a query from a file. The SQL editor features syntax coloring and autocompletion.
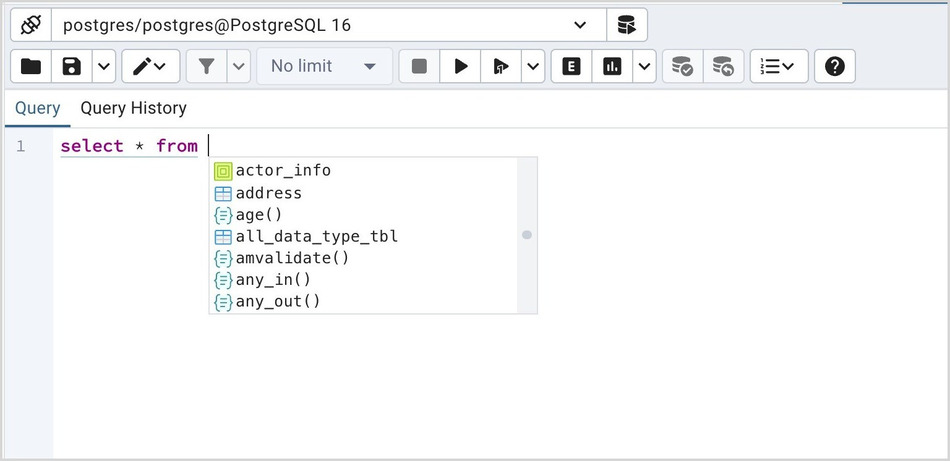
To use autocomplete, begin typing your query; when you would like the Query editor to suggest object names or commands that might be next in your query, press the Control+Space key combination. For example, type “SELECT * FROM” (without quotes, but with a trailing space), and then press the Control+Space key combination to select from a popup menu of autocomplete options.
After entering a query, select the Execute script icon from the toolbar. The complete contents of the SQL editor panel will be sent to the database server for execution. To execute only a section of the code that is displayed in the SQL editor, highlight the text that you want the server to execute, and click the Execute script icon.
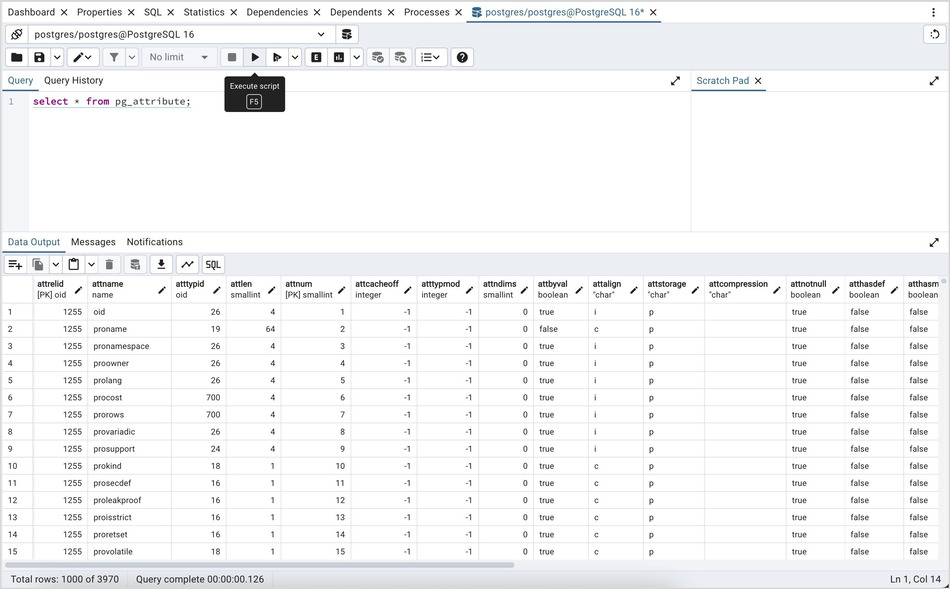
You can also execute a query based on cursor position. Query tool will detect a query and underline it when cursor position changes. Now, to execute the current underlined query, hit the Execute query button on the toolbar. If a section is highlighted then it will behave like normal execute.
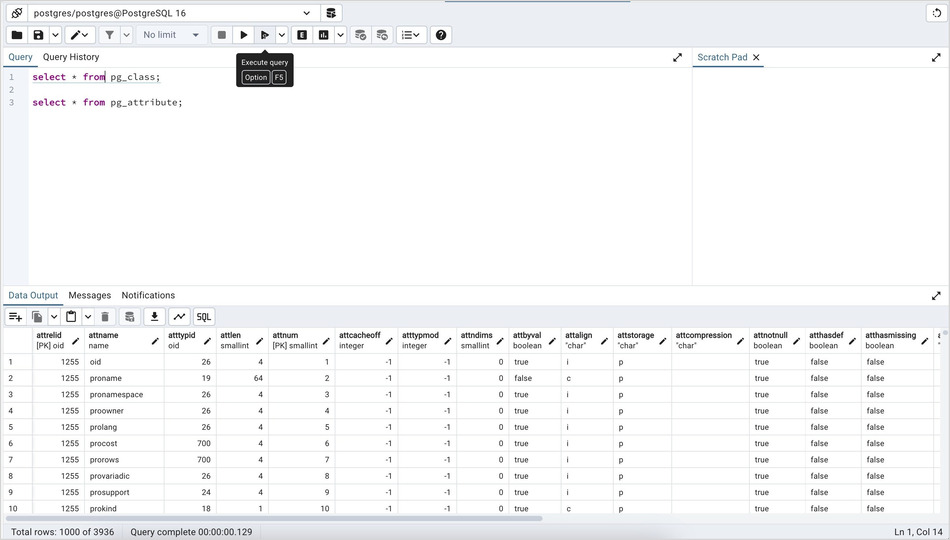
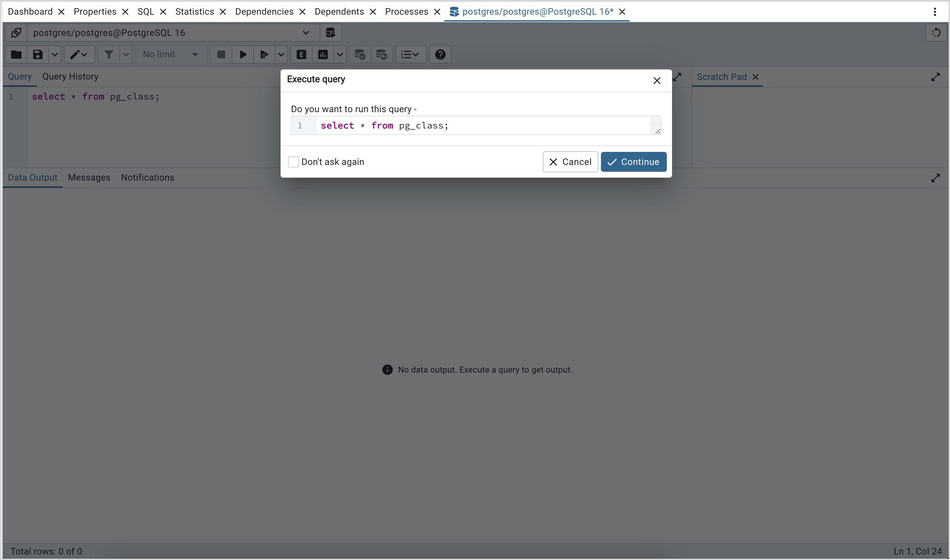
The warning will appear only if Underline query at cursor? is set to False and the Underlined query execute warning? switch is set to True Preferences Query tool’s Options.
The message returned by the server when a command executes is displayed on the Messages tab. If the command is successful, the Messages tab displays execution details.
Options on the Edit menu offer functionality that helps with code formatting and commenting:
The auto-indent feature will automatically indent text to the same depth as the previous line when you press the Return key.
Block indent text by selecting two or more lines and pressing the Tab key.
Implement or remove SQL style or toggle C style comment notation within your code.
You can also drag and drop certain objects from the treeview which can save time in typing long object names. Text containing the object name will be fully qualified with schema. Double quotes will be added if required. For functions and procedures, the function name along with parameter names will be pasted in the Query Tool.
Query History Panel¶
Use the Query History tab to review activity for the current session:
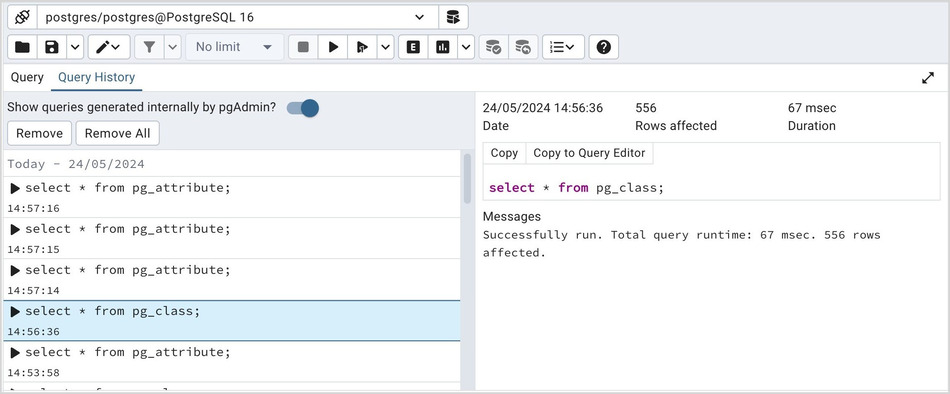
The Query History tab displays information about recent commands:
The date and time that a query was invoked.
The text of the query.
The number of rows returned by the query.
The amount of time it took the server to process the query and return a result set.
Messages returned by the server (not noted on the Messages tab).
The source of the query (indicated by icons corresponding to the toolbar).
You can show or hide the queries generated internally by pgAdmin (during ‘View/Edit Data’ or ‘Save Data’ operations).
You can remove a single query by selecting it and clicking on the Remove button. If you would like to remove all of the histories from the Query History tab, then click on the Remove All button.
By using the Copy button, you can copy a particular query to the clipboard, and with the Copy to Query Editor button, you can copy a specific query to the Query Editor tab. During this operation, all existing content in the Query Editor is erased.
Query History is maintained across sessions for each database on a per-user
basis when running in Query Tool mode. In View/Edit Data mode, history is not
retained. By default, the last 20 queries are stored for each database. This
can be adjusted in config_local.py or config_system.py (see the
config.py documentation) by overriding the
MAX_QUERY_HIST_STORED value. See the Deployment section
for more information.
The Data Output Panel¶
The Data Output panel displays data and statistics generated by the most recently executed query.
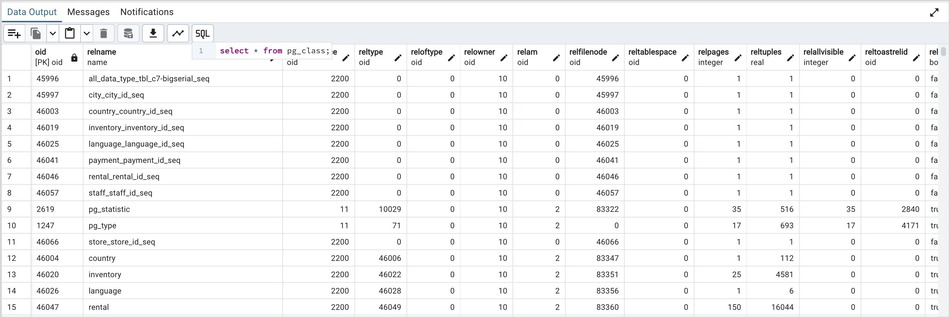
The Data Output tab displays the result set of the query in a table format. You can:
Select and copy from the displayed result set.
Use the Save results to file icon to save the content of the Data Output tab as a comma-delimited file.
Edit the data in the result set of a SELECT query if it is updatable.
A result set is updatable if:
All columns are either selected directly from a single table, or are not table columns at all (e.g. concatenation of 2 columns). Only columns that are selected directly from the table are editable, other columns are read-only.
All the primary key columns or OIDs of the table are selected in the result set.
Any columns that are renamed or selected more than once are also read-only.
Editable and read-only columns are identified using pencil and lock icons (respectively) in the column headers.
The psycopg2 driver version should be equal to or above 2.8 for updatable query result sets to work.
An updatable result set is identical to the Data Grid in View/Edit Data mode, and can be modified in the same way.
If Auto-commit is off, the data changes are made as part of the ongoing transaction, if no transaction is ongoing a new one is initiated. The data changes are not committed to the database unless the transaction is committed.
If any errors occur during saving (for example, trying to save NULL into a column with NOT NULL constraint) the data changes are rolled back to an automatically created SAVEPOINT to ensure any previously executed queries in the ongoing transaction are not rolled back.
All rowsets from previous queries or commands that are displayed in the Data Output panel will be discarded when you invoke another query; open another Query Tool tab to keep your previous results available.
Explain Panel¶
To generate the Explain or Explain Analyze plan of a query, click on Explain or Explain Analyze button in the toolbar.
More options related to Explain and Explain Analyze can be selected from the drop down on the right side of Explain Analyze button in the toolbar.
Please note that pgAdmin generates the Explain [Analyze] plan in JSON format.
On successful generation of Explain plan, it will create three tabs/panels under the Explain panel.
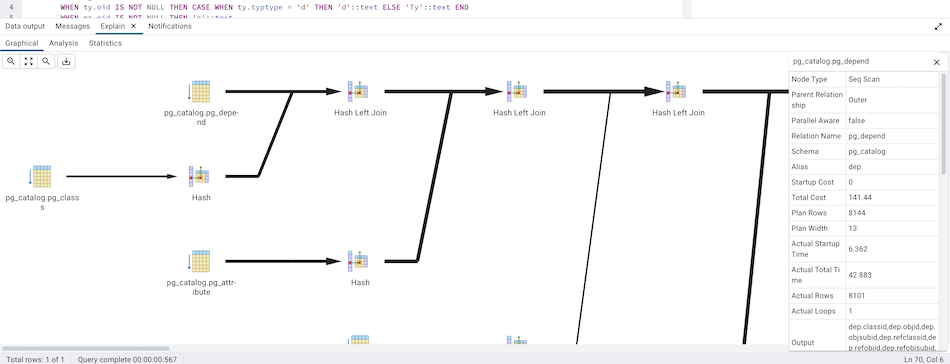
Graphical
Please note that EXPLAIN VERBOSE cannot be displayed graphically. Click on a node icon on the Graphical tab to review information about that item; a popup window will display on the right side with the information about the selected object. For information on JIT statistics, triggers and a summary, click on the button on top-right corner; a similar popup window will be displayed when appropriate.
Use the download button on top left corner of the Explain canvas to download the plan as an SVG file.
Note: Download as SVG is not supported on Internet Explorer.
Note that the query plan that accompanies the Explain analyze is available on the Data Output tab.
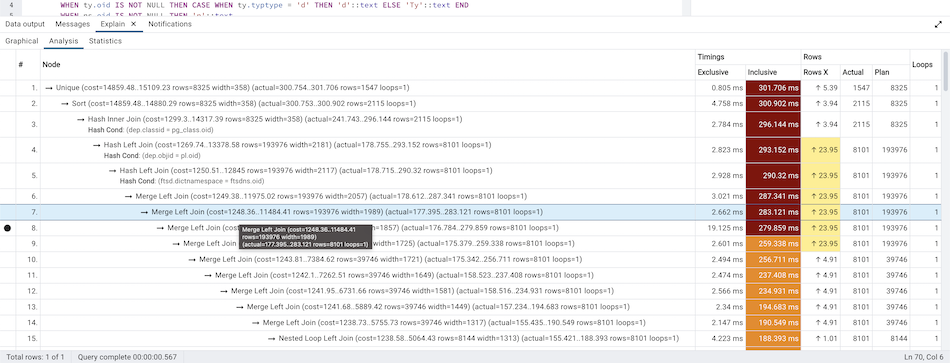
Table
Table tab shows the plan details in table format, it generates table format similar to explain.depesz.com. Each row of the table represent the data for a Explain Plan Node. It may contain the node information, exclusive timing, inclusive timing, actual vs planned rows differences, actual rows, planned rows, loops.
background color of the exclusive, inclusive, and Rows X columns may vary based on the difference between actual vs planned.
If percentage of the exclusive/inclusive timings of the total query time is: > 90 - Red color > 50 - Orange (between red and yellow) color > 10 - Yellow color
If planner mis-estimated number of rows (actual vs planned) by 10 times - Yellow color 100 times - Orange (between Red and Yellow) color 1000 times - Red color
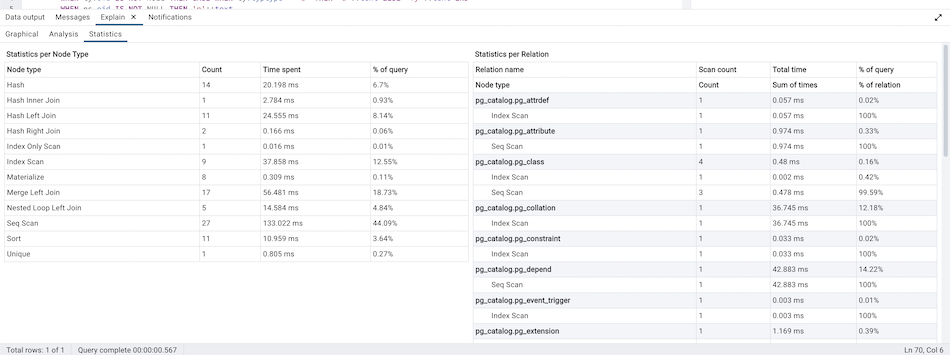
Statistics
Statistics tab shows two tables: 1. Statistics per Plan Node Type 2. Statistics per Table
Messages Panel¶
Use the Messages tab to view information about the most recently executed query:
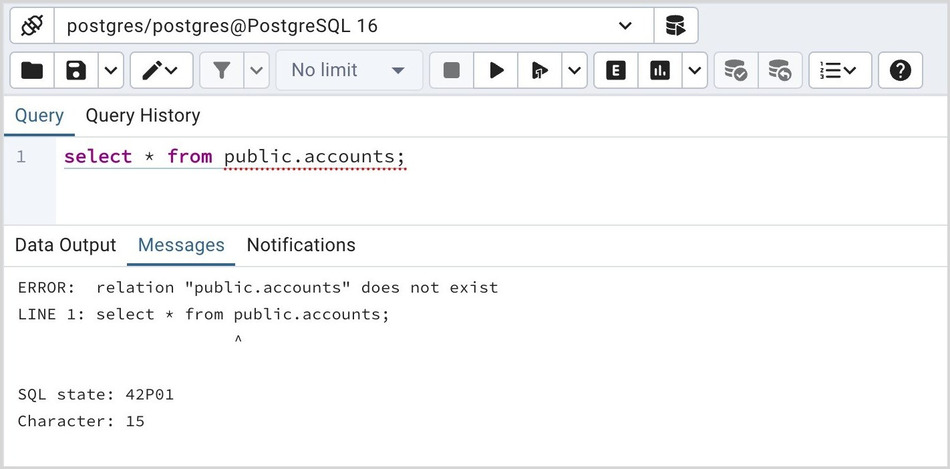
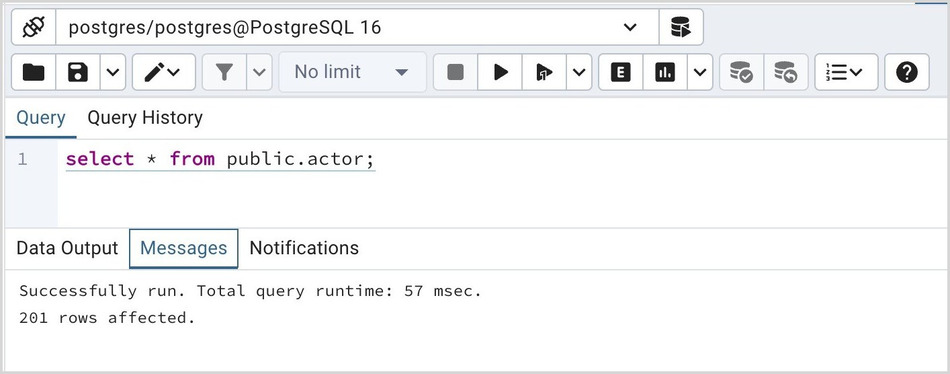
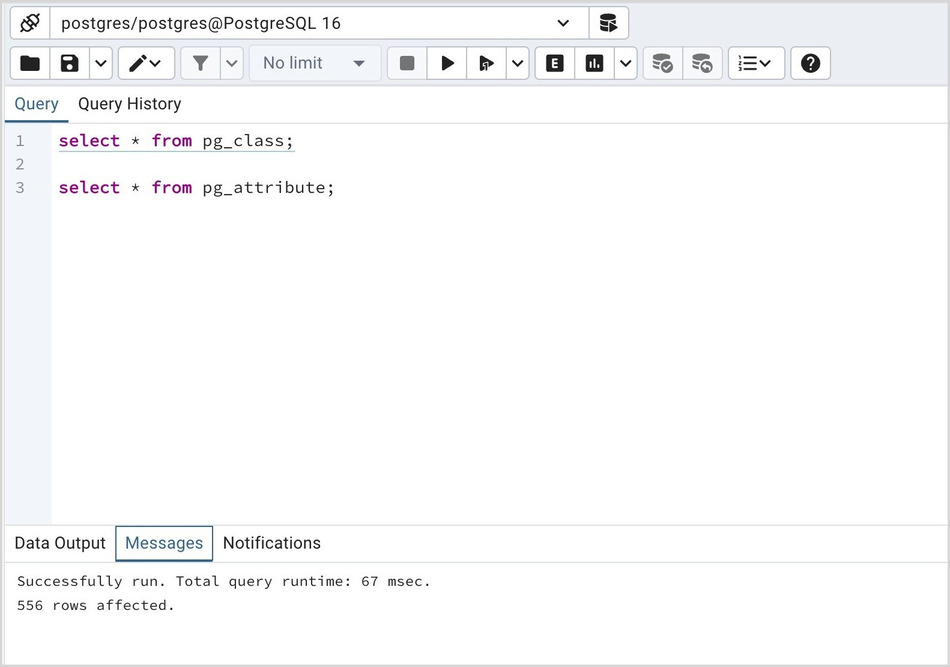
If the server returns an error, the error message will be displayed on the Messages tab, and the syntax that caused the error will be underlined in the SQL editor. If a query succeeds, the Messages tab displays how long the query took to complete and how many rows were retrieved:
Notifications Panel¶
Use the Notifications tab to view the notifications using PostgreSQL Listen/ Notify feature. For more details see PostgreSQL documentation.
Example:
Execute LISTEN “foo” in first Query Tool session
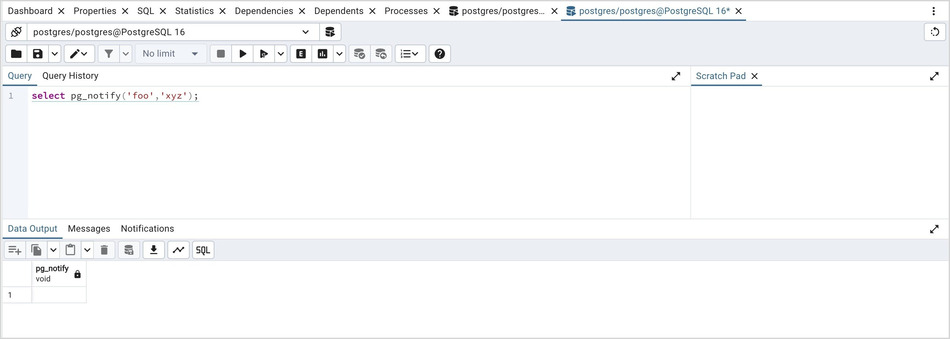
2. In the another Query Tool session, execute Notify command or pg_notify function to send the notification of the event together with the payload.
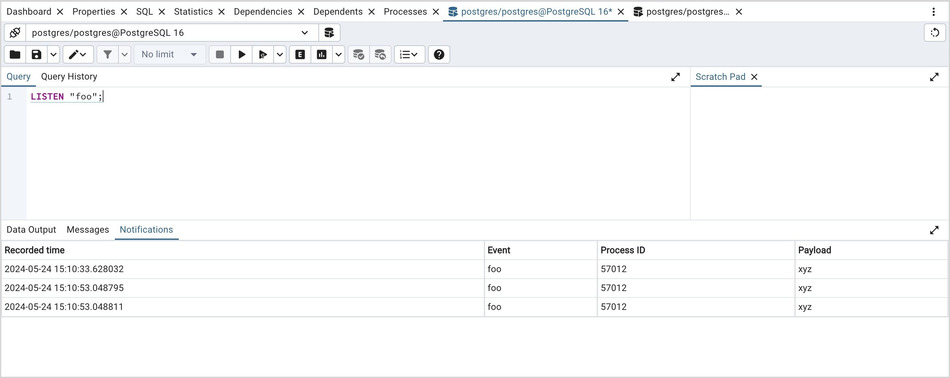
3. You can observe the Notification tab in the first Query Tool session where it shows the Recorded time, Event, Process ID, and the Payload of the particular channel.
Graph Visualiser Panel¶
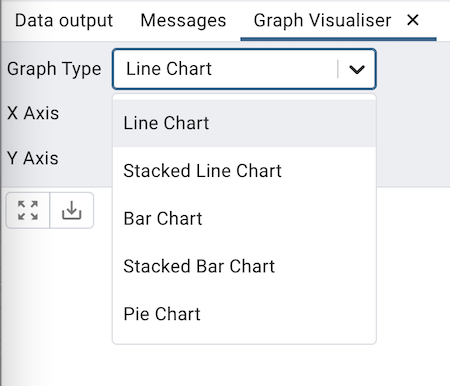
Click the Graph Visualiser button in the toolbar to generate the Graphs of the query results. The graph visualiser supports Line Charts, Stacked Line Charts, Bar Charts, Stacked Bar Charts, and Pie Charts.
Graph Type
Choose the type of the graph that you would like to generate.
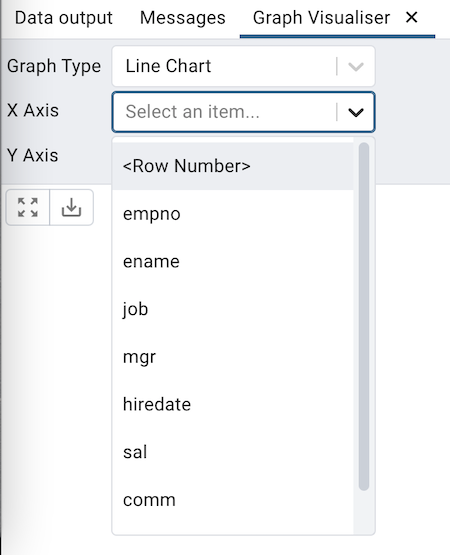
X Axis
Choose the column whose value you wish to display on X-axis from the X Axis dropdown. Select the <Row Number> option to use the number of rows as labels on the X-axis.
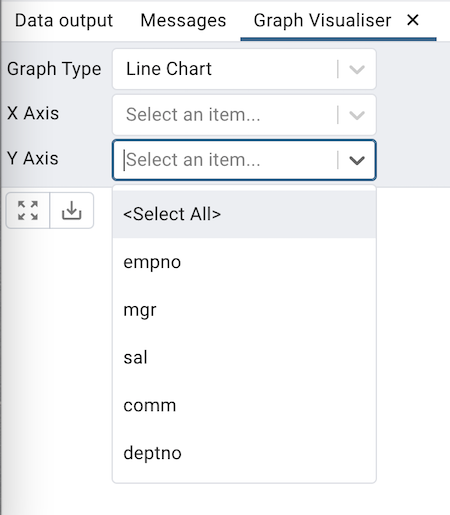
Y Axis
Choose the columns whose value you wish to display on Y-axis from the Y Axis dropdown. Users can choose multiple columns. Choose the <Select All> option from the drop-down menu to select all the columns.
Download and Zoom button
Zooming is performed by clicking and selecting an area over the chart with the mouse. The Zoom to original button will bring you back to the original zoom level.
Click the Download button on the button bar to download the chart.
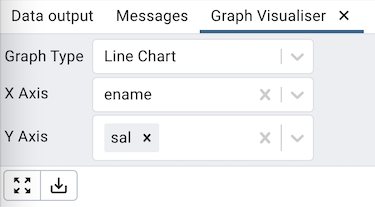
Line Chart¶
The Line Chart can be generated by selecting the ‘Line Chart’ from the Graph Type drop-down, selecting the X-axis and the Y-axis, and clicking on the ‘Generate’ button. Below is an example of a chart of employee names and their salaries.
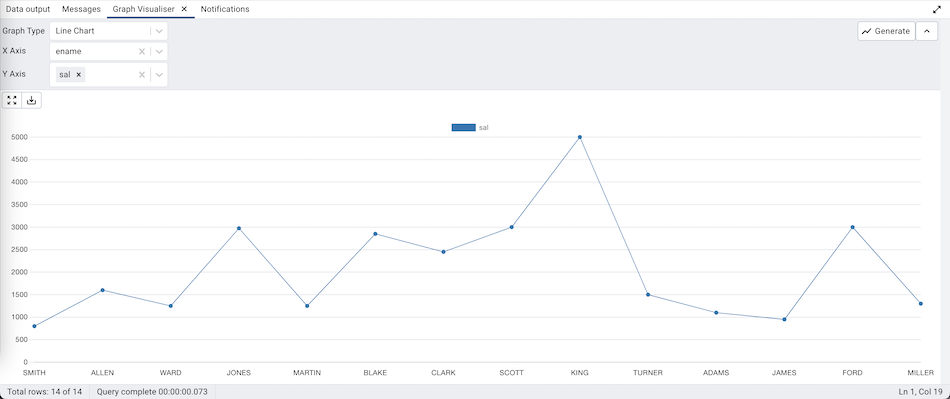
Set Use different data point styles? option to true in the Preferences Dialog, to show data points in a different style on each graph lines.
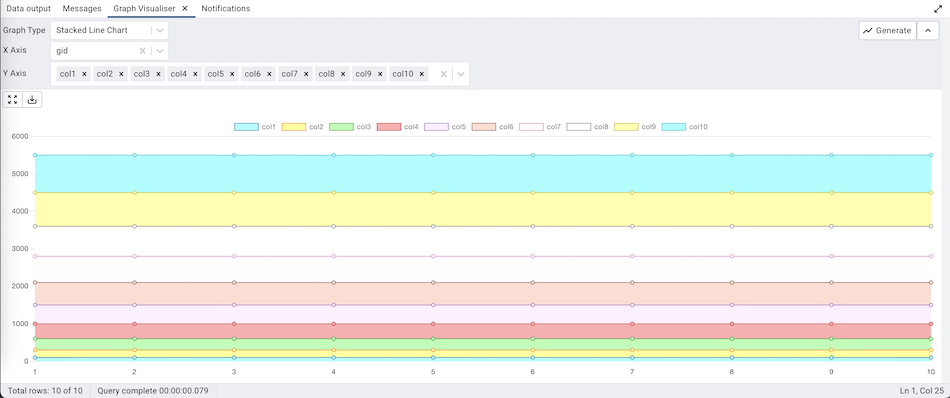
Stacked Line Chart¶
The Stacked Line Chart can be generated by selecting the ‘Stacked Line Chart’ from the Graph Type drop-down, selecting the X-axis and the Y-axis, and clicking on the ‘Generate’ button.
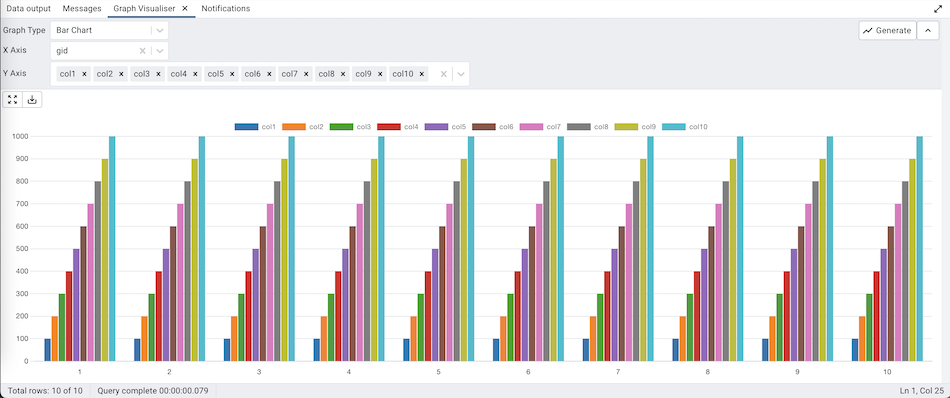
Bar Chart¶
The Bar Chart can be generated by selecting the ‘Bar Chart’ from the Graph Type drop-down, selecting the X-axis and the Y-axis, and clicking on the ‘Generate’ button.
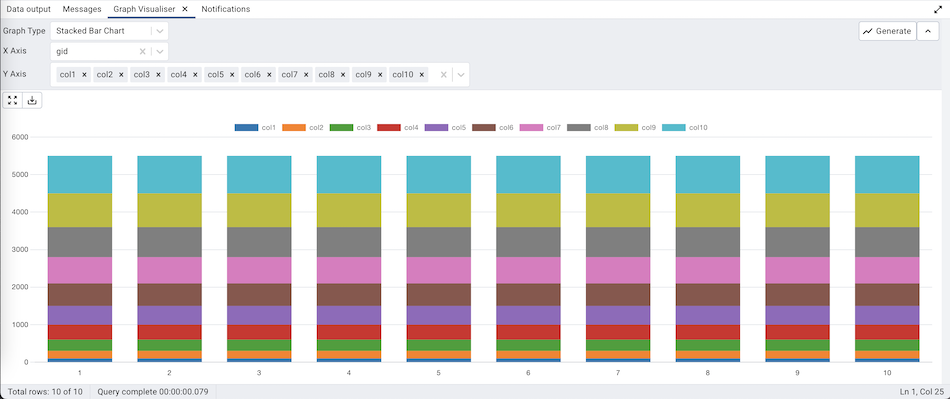
Stacked Bar Chart¶
The Stacked Bar Chart can be generated by selecting the ‘Stacked Bar Chart’ from the Graph Type drop-down, selecting the X-axis and the Y-axis, and clicking on the ‘Generate’ button.
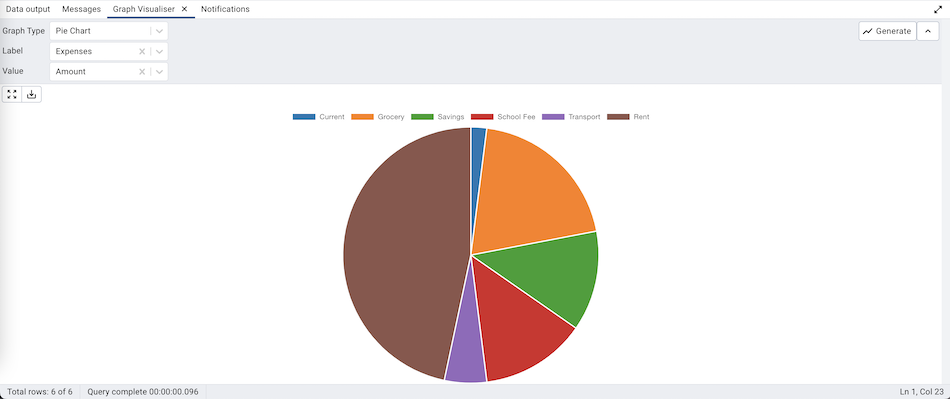
Pie Chart¶
The Pie Chart can be generated by selecting the ‘Pie Chart’ from the Graph Type drop-down, selecting the Label and Value, and clicking on the ‘Generate’ button.
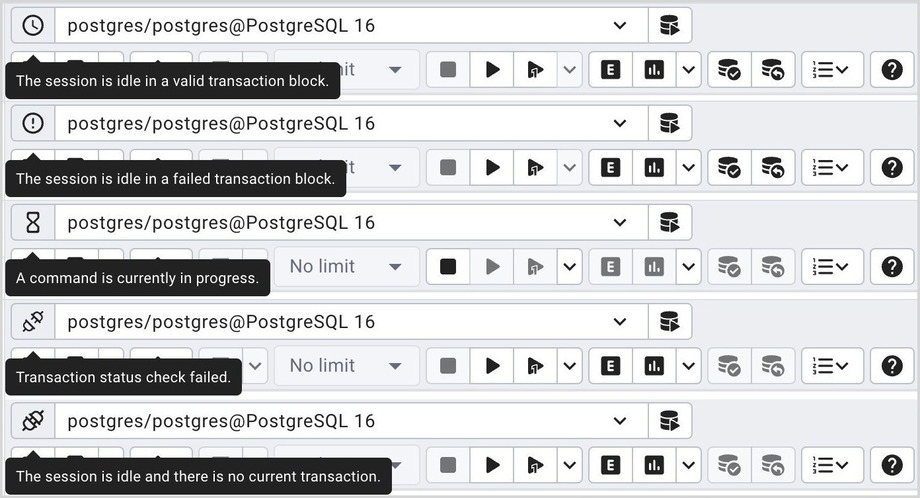
Connection Status¶
Use the Connection status feature to view the current connection and transaction status by clicking on the status icon in the Query Tool:
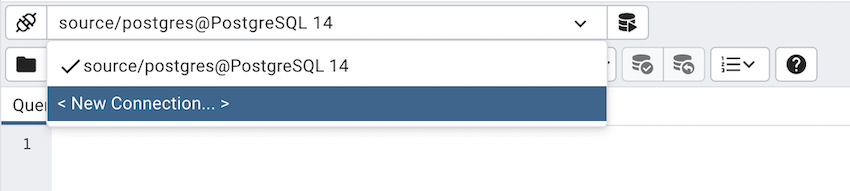
Change connection¶
User can connect to another server or database from existing open session of query tool.
Click on the connection link next to connection status.
Now click on the <New Connection> option from the dropdown.
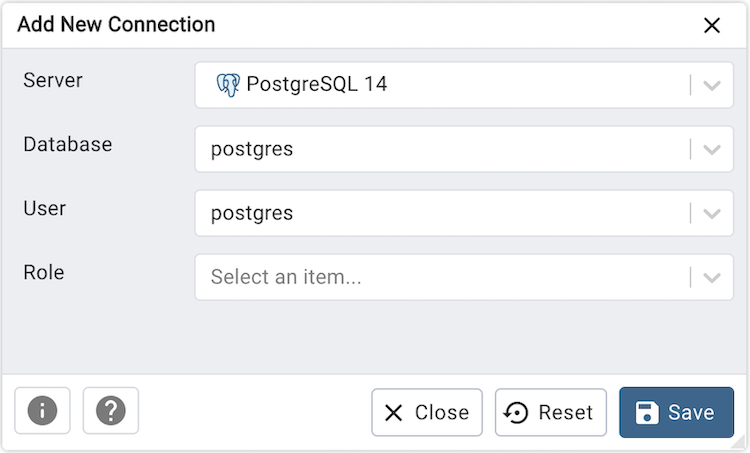
Now select server, database, user, and role to connect and click on the ‘Save’ button.
A newly created connection will now get listed in the options.
To connect, select the newly created connection from the dropdown list.
Macros¶
Query Tool Macros enable you to execute pre-defined SQL queries with a single key press. Pre-defined queries can contain the placeholder $SELECTION$. Upon macro execution, the placeholder will be replaced with the currently selected text in the Query Editor pane of the Query Tool.
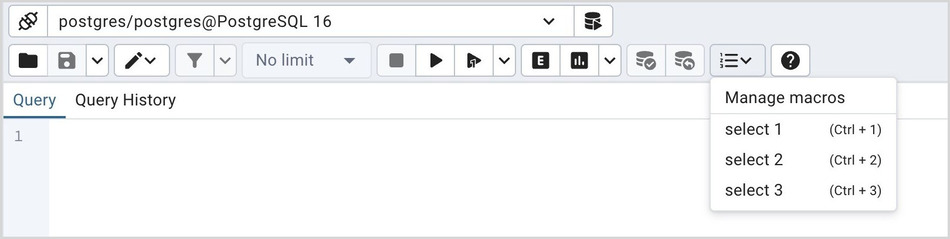
To create a macro, select the Manage Macros option from the Macros menu on the Query Tool. Select the key you wish to use, enter the name of the macro, and the query, optionally including the selection placeholder, and then click the Save button to store the macro.
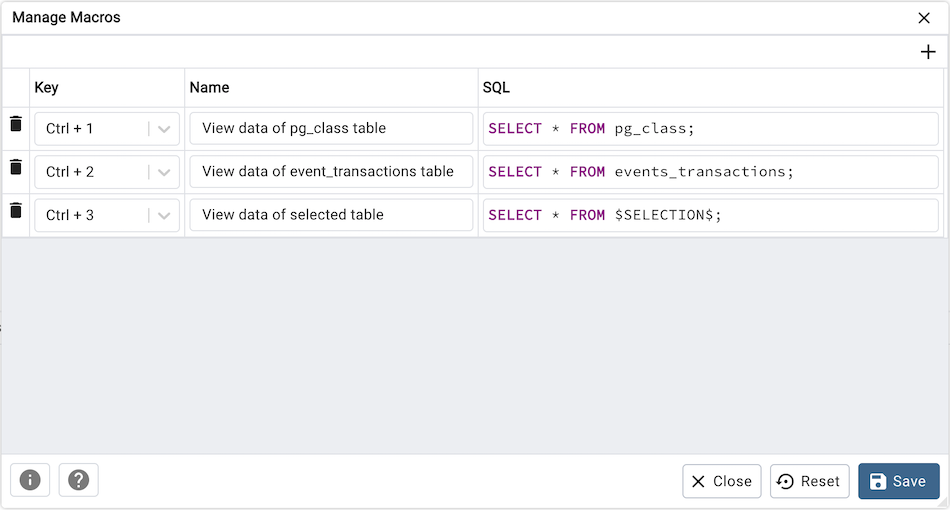
To add a query to macros, write and select your query, then go to the Macros menu in the Query Tool and click Add to macros. Your query will be automatically saved to macros.
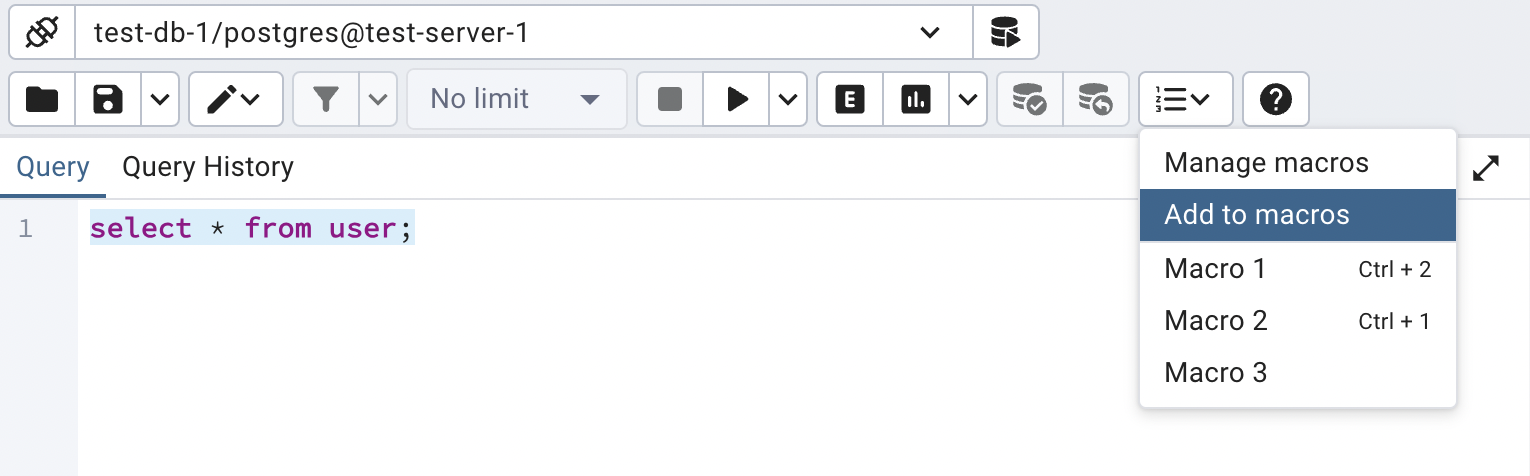
To delete a macro, select the macro on the Manage Macros dialogue, and then click the Delete button. The server will prompt you for confirmation to delete the macro.
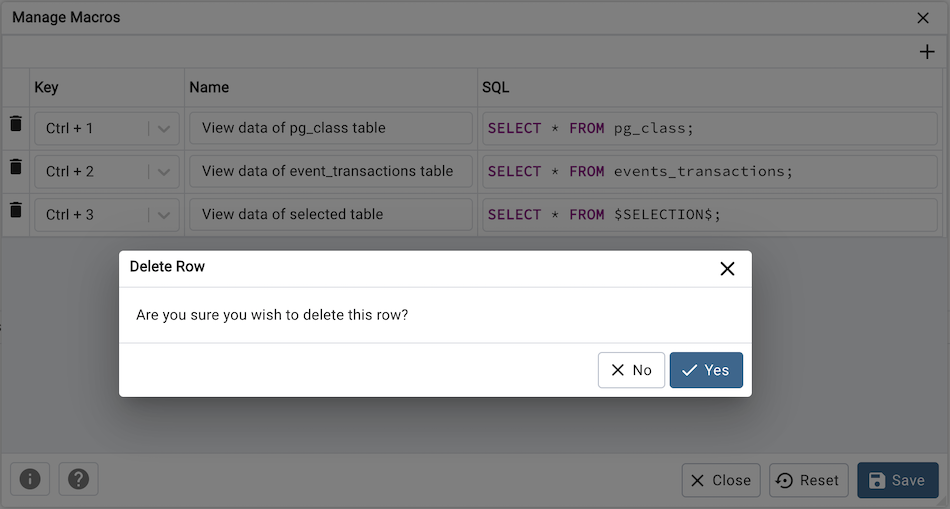
To execute a macro, simply select the appropriate shortcut keys, or select it from the Macros menu.
